A nonwoven is a fabric made of short fibers and long fibers (long, unbroken), bonded together by chemical, mechanical, thermal treatment or the use of solvents. This term is used in the textile industry to refer to fabrics such as felt, nonwoven or non-knitted fabrics.

Figure 1: Nonwoven is a fabric made of short or long fibers
General introduction of nonwoven fabrics
Nonwoven fabrics can be divided into 8 categories according to different manufacturing processes:
Spunlace nonwoven fabric
This is a product resulting from the direct use of polymer pads, short fibers or filaments to form a fiber network by gas or mechanical action, spinning, needle puncture or hot rolling, and final sewing. after finishing is spunlace nonwovens.
Applications: This fabric is known for its excellent use in masks, medical nonwoven fabrics, wet wipes, nonwoven filter cloths, etc.
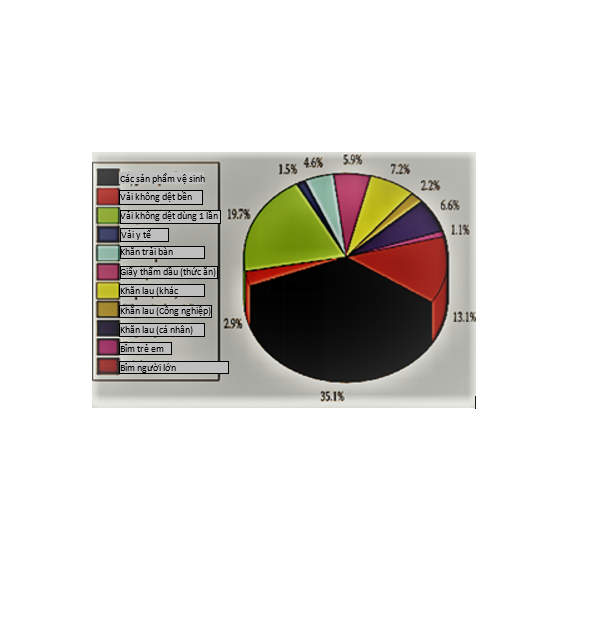
Figure 2: Distribution of nonwovens, 2014-2015
Heat-bonding non-woven fabric
This nonwoven fabric is mainly produced by a number of processes: adding a fiber filler or sticking to the fiber web, then reinforcing the network into a fabric through a process of heating and cooling.
Pulp airlaid nonwoven fabric
Pulp airlaid nonwoven fabric is also known as dust free paper, dry nonwoven fabric. It uses air-laid technology to open the wood fiber plank into a single fiber state, then uses the air flow method to agglomerate the fibers on the mesh screen and the reinforced fiber mesh to form the fabric.
Wet non-woven fabric
Wet nonwoven fabric is produced according to the following process: opening a fiber material placed in a water environment into single yarns, and concurrently mixing different fiber materials to form the yarn mixture, then mixing this is transferred to the fabrication mechanism, and the wet-state yarn is reinforced into the fabric.
Spunbond nonwoven fabric:
Spunbond nonwovens are produced by the following process: extruding and stretching polymer fibers to form continuous and meshed fibers. This mesh is then processed into a nonwoven fabric by bonding, thermal bonding, mechanical and chemical bonding.
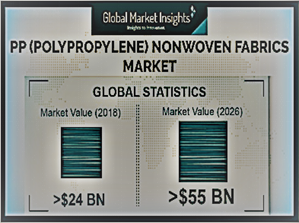
Figure 3: US market for non-woven polypropylene, 2014-2015
Meltblown nonwovens
Melblown Nonwoven Fabric is produced by extruding molten polymer fibers through a straight mold containing hundreds of tiny holes to form long thin fibers that are then stretched and cooled by letting hot air pass through as they fall. from the straight mold, this mesh is then blown into a focusing screen forming a finely filtered and self-aligned non-woven fabric. Usually this nonwoven fabric is added spunbond yarn to form SM or SMS mesh.
Non-knitted products
Non-woven knitted fabric is a dry non-woven fabric. The fine fibers are reinforced into a fabric by needle puncture.
Nonwoven stitch
Nonwoven stitching is another type of dry non-woven fabric. The manufacturing process uses a warp knit loop structure to reinforce the fiber mesh, the fiber layer, the nonwovens (such as plastic sheets, plastic foil, etc.) or a combination of them to form nonwoven fabrics.
Nonwovens market : The size of the nonwovens market is estimated to increase from $ 22.62 billion in 2016 to $ 34.85 billion by 2022. This market is expected to grow at an annual growth rate. CAGR of 7.51% over the forecast period. The baseline year is 2016, and the estimated market size is from 2017 to 2022.
Producing non-woven fabrics
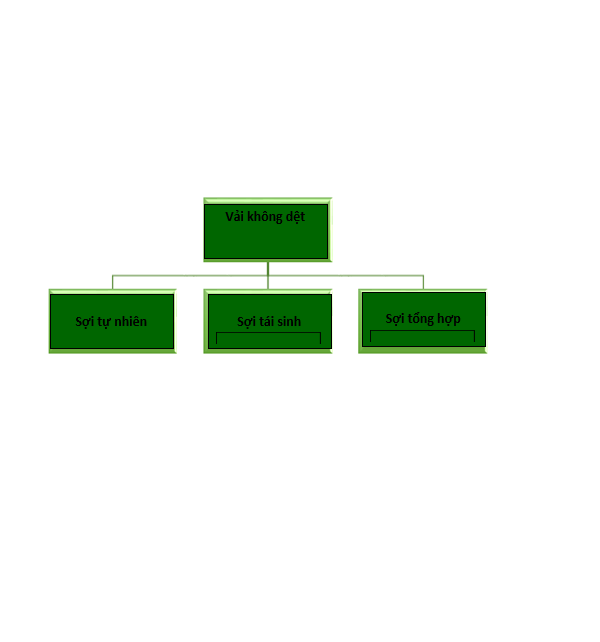
Raw material: The raw material of the non-woven fabric is shown in the diagram.
Natural fibers: cotton, jute, flax
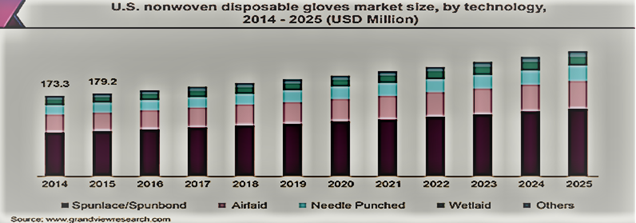
Figure 5: Market size of the US disposable nonwoven gloves for a wide variety of nonwoven fabrics.
Regenerative fiber: Bamboo fiber, viscous fiber, Tencel fiber, modal fiber.
Synthetic polymers: PP, PE, PET, NYLON, PA, polyester, PCL, PLA
Main production method of nonwoven fabric:
Felt
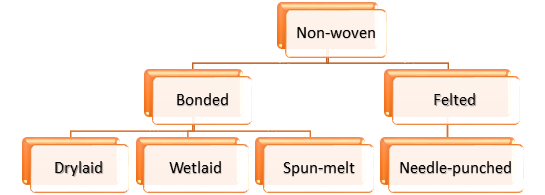
Figure 6: Nonwoven fabrication process
According to the American Testing and Materials Association ASTM, felt is a structured product consisting of the interweaving of fibers by a combination of mechanical, chemical, moisture and thermal effects without dragging. yarn, weave or knit.
Other Felt Fabrics: Cotton, jute, flax, synthetic fiber felt.

Figure 7: Multicolour Felt Fabric (Synthetic Fiber)
Manufacturing process : Felt is produced by hand or by machine. Mechanical felt production is described as follows. The yarn undergoes two successive carding operations and two card operations which result in the yarns being parallel and uniform in a fine mesh form.

Figure 8: Recycling of cotton fabrics (Geo textiles, electrical insulators)
Several mesh layers are formed until sufficient mass or thickness is accumulated. The fabric size or layer (mesh layer) is then cut and edges trimmed to the desired width. Fabric width is usually about 37m long, 150-230 cm wide and weight ranges from 8-23 kg.
The rolls are soaked with warm water, passed through the steam box to warm the fabric and pressed between the two rollers.
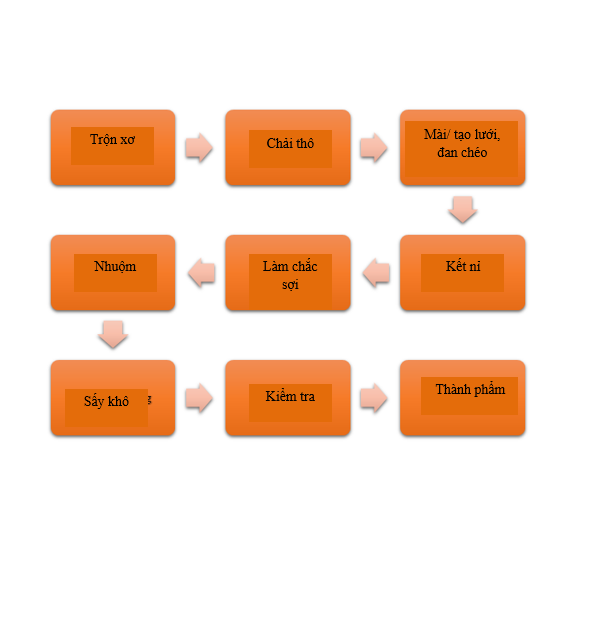
Figure 9: Non-woven fabric production
The top roller sits on the cloth and with an oscillating movement creates pressure combined with moisture and heat creating the final felting process. They are then allowed to drain and cool for about 24 hours.
Application
Geo-textile fabric: (Road construction, Construction of railway, Construction of waterways)
Mattress, sucking, floor coverings, composite.
Linked non-woven fabric:
The methods for forming nonwovens are classified according to the type of raw material chosen for the purpose of use. Short fibers and filaments are used to make nonwovens.
Non-woven fabric manufacturing techniques include:
Dry Film Forming : Dry- film is one of the older techniques and very similar to the felt-wrap process. For the production of dry film, cards and net tilling machines are used to coat the fiber film. The fibrous lattice layers are then softened using heat, moisture and vibrations. These materials may have a natural or synthetic polymer composition and may be processed alone or in a mixture. Card webs are manufactured from short yarn (20–60 mm) or long yarn (50–150 mm).
Dry film-making techniques, such as yarn preparation, blending, carding and fabric weaving, are innovations in the textile industry. These processes prepare the base fibers, blend them and lay the fibers in a dry state. During dry mesh formation, the fibers are collected lattice by parallel winding, criss-cross, or an aerodynamic ring (air-laid) and then bonded with a mechanical needle, fiberglass wrapping, chemical binder and heating methods.
Raw materials: Cotton fiber, synthetic fiber, Viscose fiber, cotton short fiber.
Application of the dry method:
Wet-film formation : Wet- film formation is considered similar to conventional paper production, but using synthetic fibers or shredded short fibers. This method continues to gain attention as it is seen as a convenient way to prepare advanced nonwovens. The wet film forming system is designed to fabricate short fibers that are dispersed in the liquid, then layered. The wet spreading method is especially suitable for the large-scale production of disposable products, such as tea bags, aprons, gloves, napkins and surgical dressings.
Raw material: A wide variety of natural fibers, wood pulp, mineral fibers, synthetic fibers and man-made fibers of different lengths such as glass, polyester, polyamide and recycled fiber can be used.
Applications: Filter paper, tea bags, napkins, surgical gauze.
Fusible Spun Nonwoven: Fusible Spinning is a general term describing the manufacture of nonwovens directly from thermoplastic polymer fibers. It consists of 2 processes:
Spinning (bonding) nonwovens: Polymer particles are extruded into fibers through yarns. The fibers are continuously stretched and cooled before being fed into the conveyor to form a homogeneous network. The spinning process produces nonwovens with higher strength than carding, due to weakening of filaments. The downside is that the choice of raw materials is more limited. Co-extrusion of the two components results in bico fibers being added to more properties to the mesh or to allow for air bonding. Note that the term spunbond is reserved for the thermal bonding method of spinning.
Raw material: PP (polypropylene), Pet, Nylon, PE, Polyester. (Synthetic thermoplastic).
Production process:
Application: Packaging (Shopping Bag), PPE for medical medical
Melt Blown Nonwoven: The Meltblown method, like spun, begins with the extrusion of a low viscosity polymer. But instead of quenching the fibers as they leave the camera, the fibers are weakened by hot air currents, keeping the fibers partially molten. This results in much thinner fibers, with low tension. These fibers hit a conveyor or conveyor belt, where they form a network.

Figure 10: Application of nonwovens in railway, road and riverbank constructions
Raw material: Polypropylene (PP), polyamide (PA), Polyester, Polyethylene (PE).
Some of the treated polymers:
Manufacturing process : The melblown technology is based on a fusion blow process, in which, normally, a thermoplastic fiber-forming polymer is extruded through a straight mold containing several hundred tiny holes. Converging hot air streams rapidly weaken the flow of extruded polymers to form extremely fine fibers (1-5 micro / meter). The degraded fibers are then blown by high viscosity air onto a collection conveyor, where they form a fine fiber self-bonding nonwoven fabric.
Applications: Filter paper, N95 mask (as filter cloth), PP gown, surgical mask, napkin, tea bag, water filter.
Face mask
N95 respirator: N95 respirator is a respiratory protective device designed to achieve a tight face and effectively filter airborne particles.
The designation 'N95' means that when carefully tested, the respirator blocks at least 95 percent of very small (0.3 micron) test particles. If used correctly, the N95 respirator's filtering ability will far exceed that of conventional respirators. However, even a properly used N95 respirator does not completely eliminate the risk of illness or death. Surgical N95 respirators are commonly used in healthcare settings and are a sub-product of N95 filter cloth.
Production technology : 5-layer fabric.
Surgical respirator: A surgical respirator is a disposable, disposable device that creates a physical barrier between the wearer's mouth and nose and potential contaminants in the surrounding environment. These are often called masks, although not all types of masks are considered surgical masks.
Production technology:
Raw material: SMS fabric for 3-layer surgical mask.
Fabric production process of SMS-spinning, blowing-melting-spinning binder.
https://vinatex.com.vn/cac-loai-vai-khong-det-ung-dung-va-quy-trinh-san-xuat/
Source: vinatex.com.vn